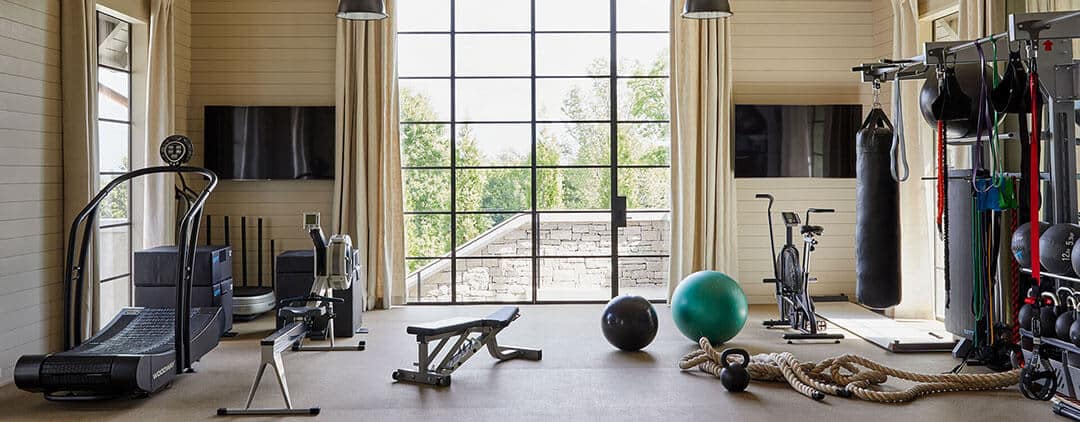
Free weight training is a fundamental aspect of fitness that has stood the test of time. Unlike machine-based exercises, free weights allow for natural movement patterns, which can improve overall strength, flexibility, and coordination. This guide is designed for both beginners and experienced trainees who want to understand the benefits and techniques of using dumbbells, Olympic barbells, and other free weights.
Whether you’re just starting your fitness journey or looking to enhance your current routine, this article will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to succeed.
Part 1: Understanding Free Weights
What Are Free Weights? Free weights are exercise equipment that allows you to move through a full range of motion without being restricted by a machine. Common examples include dumbbells, barbells, and kettlebells. These tools mimic real-life movements, making them highly effective for functional fitness and athletic performance.
Benefits of Free Weight Training:
- Increased Muscle Strength and Endurance: Free weights engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater overall strength gains.
- Improved Joint Flexibility: The natural movement patterns used in free weight exercises help maintain and improve joint health.
- Enhanced Balance and Coordination: Since you control the weight’s path, free weights require more core engagement and stability, improving balance and coordination.
- Higher Calorie Burn: The additional effort required to stabilize the weight during free weight exercises can lead to increased calorie expenditure.
Part 2: Dumbbells
Types of Dumbbells:
- Fixed-Weight Dumbbells: These come in pre-set weights and are ideal for home gyms or commercial settings.
- Adjustable Dumbbells: These allow you to change the weight by adding or removing plates, providing versatility in your workouts.
Advantages of Dumbbell Training:
- Versatility: Dumbbells can be used for a wide range of exercises, from basic to advanced.
- Isolation of Muscle Groups: They are excellent for targeting specific muscles, such as biceps, triceps, and shoulders.
- Ease of Storage and Portability: Dumbbells take up less space and can be easily transported.
Recommended Dumbbell Exercises:
- Bicep Curls: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, hold dumbbells at your sides, and curl them toward your shoulders.
- Shoulder Press: Hold dumbbells at shoulder height, then press them overhead until your arms are fully extended.
- Lateral Raises: Stand with feet hip-width apart, hold dumbbells at your sides, and raise them to shoulder height.
Safety Tips:
- Start with Light Weights: Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with the movements.
- Maintain Proper Form: Focus on controlled movements to avoid injury.
- Use a Spotter if Needed: For heavier lifts, having a spotter can provide added safety.
Part 3: Olympic Barbells
Features of an Olympic Barbell:
- Rotating Sleeves: Allow the weights to rotate freely, reducing stress on the wrists and elbows.
- Standard Diameter: Typically 28mm for men and 25mm for women, ensuring compatibility with various types of weight plates.
- Weight: Standard Olympic barbells weigh 20kg (44lbs) for men and 15kg (33lbs) for women.
Advantages of Olympic Barbell Training:
- Compound Movements: Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses engage multiple muscle groups, promoting efficient workouts.
- High-Intensity Training: Suitable for advanced lifters and competitive athletes who require heavy lifting.
- Functional Strength: Mimics real-world movements, enhancing overall physical performance.
Recommended Olympic Barbell Exercises:
- Squats: Place the barbell on your upper back, stand with feet shoulder-width apart, and lower your body as if sitting in a chair.
- Deadlifts: Stand with feet hip-width apart, bend at the hips and knees to grasp the bar, then lift it to a standing position.
- Bench Press: Lie on a bench, grasp the bar with a shoulder-width grip, and press it upward until your arms are fully extended.
- Clean and Jerk: A complex movement involving lifting the bar from the floor to the shoulders, then pressing it overhead.
Safety Tips:
- Warm-Up Thoroughly: Spend time warming up your muscles and joints before heavy lifting.
- Use Proper Technique: Ensure you have a good understanding of the form for each exercise.
- Start with Lighter Weights: Gradually increase the load as you build strength and confidence.
Part 4: Creating a Free Weight Training Plan
How to Develop a Personalized Training Plan:
- Set Clear Goals: Whether it’s building muscle, increasing strength, or improving endurance, define what you want to achieve.
- Choose the Right Frequency and Intensity: Beginners might start with 2-3 sessions per week, while advanced lifters can handle 4-5 sessions.
- Balance Your Workouts: Include exercises that target all major muscle groups to ensure balanced development.
Beginner’s Guide:
- Sample Workout Routine:
- Day 1: Upper Body
- Dumbbell Bench Press: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Dumbbell Rows: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Lateral Raises: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Day 2: Lower Body
- Goblet Squats: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Dumbbell Deadlifts: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Calf Raises: 3 sets of 15-20 reps
- Day 3: Core and Full Body
- Planks: 3 sets of 30-60 seconds
- Russian Twists: 3 sets of 20 reps
- Dumbbell Lunges: 3 sets of 10 reps per leg
- Day 1: Upper Body
Advanced Training Challenges:
- Increase the Load: Gradually add more weight to your lifts.
- Try New Techniques: Incorporate drop sets, supersets, and pyramid training to challenge your muscles.
- Focus on Recovery: Ensure you get enough rest and nutrition to support your training.
Part 5: Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Overtraining:
- Signs of Overtraining: Persistent fatigue, decreased performance, and mood changes.
- Prevention: Balance your training with adequate rest and recovery days.
Neglecting Warm-Ups and Cool-Downs:
- Importance: Warming up increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for activity. Cooling down helps reduce muscle soreness and stiffness.
- Proper Techniques: Dynamic stretches before workouts and static stretches after.
Incorrect Technique:
- Risks: Poor form can lead to injuries and limit your progress.
- Correction: Seek guidance from a certified trainer or use online resources to learn proper technique.
Conclusion
Free weight training offers numerous benefits for physical health and performance. By understanding the basics of dumbbells and Olympic barbells, you can create a well-rounded training plan that suits your goals and fitness level. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced lifter, the key is to start with the right foundation and gradually build your skills and strength.